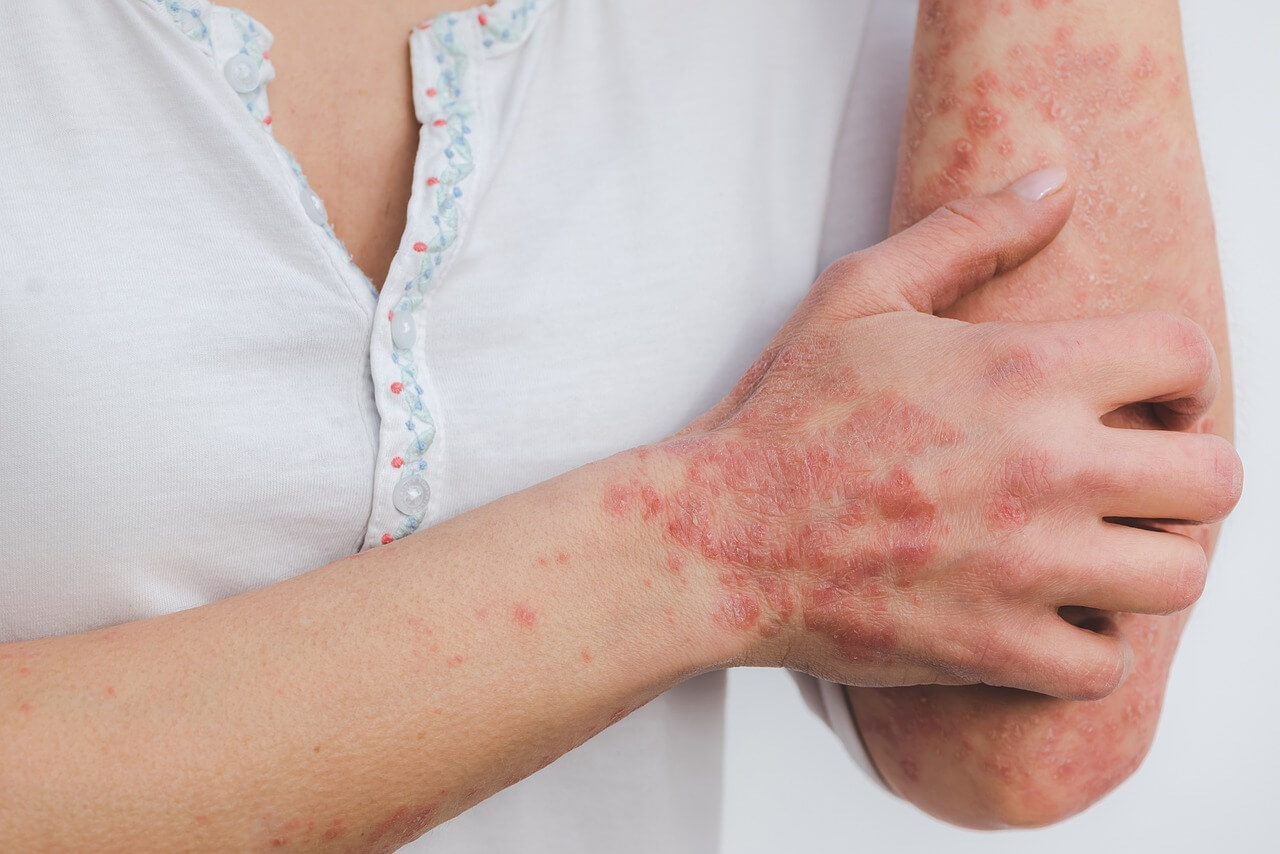
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that affects the skin, causing an accelerated growth of skin cells, triggered by an over-active immune system. This leads to the formation of thick, red patches known as plaques, which are often accompanied by itching, pain, and sometimes even joint inflammation. Despite being non-contagious, psoriasis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, both physically and emotionally. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the symptoms, causes, therapy, and treatment options for psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis presents itself in various forms, each with its unique symptoms:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells (scales). These patches can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Typically appears as small, dot-like lesions on the trunk, limbs, and scalp. It often occurs suddenly and can be triggered by bacterial infections such as strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Manifests as smooth, red lesions in skin folds such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. It tends to worsen with friction and sweating.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin. This form can be localized to certain areas of the body or widespread.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe and rare form of psoriasis that leads to widespread redness, swelling, and shedding of skin. It can cause severe itching and pain and may require immediate medical attention.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Some key contributors include:
- Genetics: Psoriasis tends to run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- Immune System Dysfunction: In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering an inflammatory response and accelerating the growth cycle of skin cells.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors such as stress, infections, injuries to the skin, certain medications, and hormonal changes can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
Therapy/ Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis management typically involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing inflammation, controlling symptoms, and preventing flare-ups. Common treatment approaches include:
- Topical Treatments: These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, and coal tar preparations, which are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and promote the shedding of dead skin cells.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. UVB phototherapy and PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) are the most common forms of light therapy used for psoriasis.
- Systemic Medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral or injected medications may be prescribed to target the underlying immune system dysfunction. These may include methotrexate, cyclosporine, biologics, or newer small molecule drugs.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding triggers such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and following a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce psoriasis symptoms.
Is there a Cure?
While there is currently no known cure for psoriasis, ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the condition, leading to improved treatment options. Additionally, many individuals experience periods of remission where symptoms improve or disappear entirely.
Some promising areas of research include:
- Biologics and Targeted Therapies: These medications specifically target the immune system pathways involved in psoriasis, providing effective symptom relief with fewer side effects compared to traditional systemic medications.
- Gene Therapy: Emerging treatments aim to modify genes associated with psoriasis susceptibility, potentially offering long-term relief by addressing the underlying genetic factors.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Investigational studies are exploring the use of stem cells to regenerate healthy skin cells and modulate the immune system, offering a novel approach to psoriasis treatment.
- Precision Medicine: Advancements in genomic profiling and personalized medicine may lead to tailored treatment approaches based on individual genetic makeup and disease characteristics.
In conclusion, psoriasis is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the symptoms, causes, therapy, and treatment options available, individuals affected by psoriasis can work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an effective treatment plan tailored to their needs, ultimately improving their quality of life and well-being.
Disclaimer: As a service to our readers, MVS Pharma GmbH publishing provides access to our library of archived content — in our blog. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.